Youtube: Forms in 25 minutes
How to structure a web form 🔗
Learning Objectives
Link to the coursework
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Forms/How_to_structure_a_web_form
Why are we doing this?
We are using HTML to explore the ideas of describing data clearly and systematically. We are building our understanding of data structures in preparation for learning JavaScript and Python. We all learned some HTML during ITD so this is a convenient structured medium to practice these concepts.
Maximum time in hours
1
How to get help
Share your blockers in your class channel https://curriculum.codeyourfuture.io/guides/getting-help/asking-questions/
How to submit
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Forms/Test_your_skills:_Form_structure
Schedule your study notes according to the spaced repetition advice and now use what you’ve learned to complete the Form Controls coursework.
Spaced Repetition
What are we doing now?
You’re going to use this prep time to answer some questions and schedule in times to review your understanding. In your planner or calendar, schedule a short (10 minute) review of your answers:
💡Space at increasing intervals
- One week from today
- One month from today
- Three months from today
- Six months from today
- One year from today
Do this now. Then move forward to working through as many of these questions as you can. (You may not complete them all, and that is ok.)
Write down your answers first and then update them after looking at the sample answers, if it’s useful to do so. Use all available tools to help you answer, and remember:
the point is not to complete the exercises the point is for you to secure your own understanding
Examples of tools you might use
What are forms?
Learning Objectives
These questions and answers are compiled from recorded sessions on HTML forms, and are the collective contribution of several mentors and students. This time we’ve included a trainee answer and a mentor answer, per question.
10 Things About Forms
So let's go deep on forms. What is a form? What does form mean?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: What does form mean? It’s like a set of options for a user to choose from on a website.
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Yes, that is true, that is a correct answer. A deeper answer might be form means shape. It’s how we define the shape of data. So, imagine a shape sorter. You put a square thing in the square hole; you put a round thing in the round hole. Each form field is a different shape in the shape sorter lid. That’s what we’re doing when we write forms. We are forming data with fields.
Why do we do that? Why do we bother grouping and shaping data in that way?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: Of course because it makes it easier to sort it out.
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Yeah, absolutely! Because you know we’re going to post that data to a database. Our database doesn’t know what all these strings mean. We have to define the data. We have to label the data. We have to group it, and we have to do something with it: to post it to a database or in some cases, get it from a database.
So that’s the point of all this.
What does field mean?
👩💻💬 Trainee: Field? It means like the window is completed with some information. A piece of data.
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Right! You put a piece into a form field; you just put one thing in there. A form has many fields, and a field is a single piece of data. It is the smallest piece.
So we structure data with forms. And we do that by defining form fields with semantic HTML.
📝Now practise with
What else do we structure, when we write an HTML form?
🧑🏻💻💬 Trainee: Gathering data you mean? I’d be doing a search…
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: Can I say? We can structure… an action, a connection.
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Ooh, that’s a great answer. We can structure interaction. We tell the user, what to put in the form field, and how to put that data in. We structure a really specific kind of interaction. We guide them and tell them what to do. And the way that we structure those interactions is, again, using form fields. Using HTML form elements, attributes, and values.
That’s really important to think about, because when you’re deciding what to write in a form, you need to start with ‘what data do I need.’ It’s better to do that than to try and memorise all the different types of form fields. If you think:
Then look up that last part. That’s more effective than trying to memorise all the different types of form fields.
But saying that, let's name some form fields now -- some elements in HTML that we can use to structure data. I'm going to say, input of type text. Name a bunch more.
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: Yeah, maybe checkbox?
👩🏼💻💬 Trainee: radio button.
👨🏿💻💬 Trainee: submit input type, could be submit or button itself.
👩🏽💻💬 Trainee: autocomplete?
👨🏻💻💬 Trainee: I think autocomplete is an attribute, but it’s not itself an element or element type? How about textarea ?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: select and option
👨💻💬 Trainee: The input of type password…
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: The point being that there are absolutely loads of different form elements!
What you need to focus on is what you’re actually doing. We’re structuring data: you are defining, naming and then grouping data. Keep that goal front and center, then your forms will work well.
📝Now practise with
Oh and... what does input mean?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: Input means to put something in. In this case the data we put in the form.
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Bang on.
What happens when things don't work well. What happens when the user puts the wrong thing in a field?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: Do you mean validation? Don’t we need JavaScript for that?
🧑🏾💻💬 Mentor: We’ll learn about validation with JavaScript later on, but there’s actually a lot of validation built in to HTML. For example, if you put a required attribute on a field, the browser will not let you submit the form until you fill in that field. That’s validation: it checks against rules and rejects the data if it doesn’t meet the rules.
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: But then aren't all form elements validation?
🧑🏽💻💬 Mentor: You could say that all the rules you make about what the user can put in a field are also validation. Every type we just named - input type checkbox, input type email, number, date… are rules about data.
I think the difference is that there’s no way to type into a checkbox: there’s no error message, you just can’t do it. If you type your birthday into an email field, the browser will tell you that’s not a valid email address. So one is just impossible to do and the other gives you an error message, and that’s normally what we mean by validation.
Why is it important to validate data?
👨🏻💻💬 Trainee: Because if you don’t validate it, you might not be able to use it?
🧑🏾💻💬 Mentor: Right. Forms go wrong when you are vague. You must enforce input with validation, because if users can get it wrong, they will.
What will happen if you put a type of text on an input you label with email?
👨🏾💻💬 Trainee: Oh well then people will write in things that aren’t email addresses?
🧑🏿💻💬 Trainee: And you won’t know until you try to send them an email…
👩🏻💻💬 Mentor: Yeah they will. You can be absolutely guaranteed that users will do that. You have to save them from themselves, and save your database from your users!
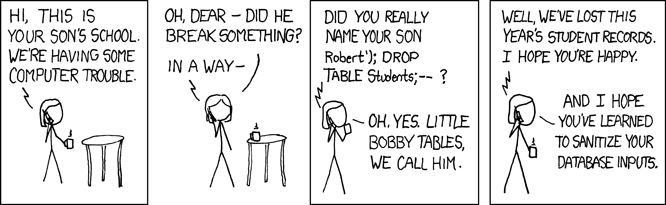
📝Now practise with
Youtube: Google Sheets Query Function Explained
Databases with Google Sheets
Learning Objectives
What is a database?
A database is a structured set of data held in a computer. It stores, retrieves and organizes information.
You already use databases in your everyday life! A few examples:
- The messages you send on Slack are stored in a database.
- CYF stores your name and email on a database!
- Your phone contact list? That will be in a database too!
What else you do on your computer and phone? What information is there? And where do you think it’s stored? Write down five other databases you get information from.
How do they work?
Most databases arrange data into columns and rows.
| column 1 | column 2 |
|---|---|
| row 1 | row 1 |
| row 2 | row 2 |
A row is a single record of this information which is grouped together, for instance, information about one person.
Within a row, each column stores a property of that record. In the example of your phone’s contact list, this would be name and number. Each row (or record) has a name and a number. What other properties does your address book store? Open your phone and take a look.
| First Name | Surname | Mobile Number |
|---|---|---|
| Tom | Jones | +447700000 |
| Ali | Smith | +327700000 |
Tom and Ali’s details here are records in the database. The properties are listed as columns and the values are in rows. Each row is a new record.
If you’ve used tools such as Excel or Google Sheets, you will have seen this sort of structure before. We’ll take a closer look at these in the backlog exercises for this module. You’ll learn how to manipulate data in Google Sheets and use SQL syntax to retrieve information from databases.
Backlog
Learning Objectives
In software development, we break down complex projects into smaller, manageable parts, which we work on for a week or two. These periods are called “sprints.”
A sprint backlog is like a to-do list. It lists what the team has decided to work on this sprint. It’s chosen from a larger list, usually called the “product backlog,” which holds the entire project to-do list.
In this course, the backlog is a set of work designed to build understanding beyond the concepts introduced in the course prep. For your course, we have prepared a backlog of mandatory work for each sprint. You will copy these tasks into your own backlog. You can also add any other tickets you want to work on to your backlog, and schedule all of the tasks according to your own goals and capacity. Use your planning board to do this.
You will find the backlog in the Backlog view on every sprint.
Copy the tickets you are working on to your own backlog. Organise your tickets on your board and move them to the right column as you work through them. Here’s a flowchart showing the stages a ticket goes through:
🕹️Backlog (30 minutes)
- Find the sprint backlog
- Copy your tickets to your own backlog
- Organise your tickets on your board